In my years in the steel packing industry, I've seen a common problem that costs mills a lot of money. A steel mill in Indonesia might produce top-quality coils, but if the final package is weak, all that hard work is wasted. You ship a perfectly good coil, but it arrives at your customer's facility with shifted layers or edge damage because a strap was too loose or too tight. This leads to customer complaints, expensive claims, and damage to your hard-earned reputation. It’s a frustrating cycle where a small detail in the final step of production undermines the entire process.
Advanced strapping heads enhance quality on Indonesian steel coil packing lines by delivering precise and consistent strap tension, creating stronger and more reliable seals, and integrating with automation systems. This precision minimizes the risk of coil telescoping and edge damage. The result is a secure, stable package that protects the coil's integrity from the factory floor to the final destination, ensuring it meets strict quality standards for transport and storage.
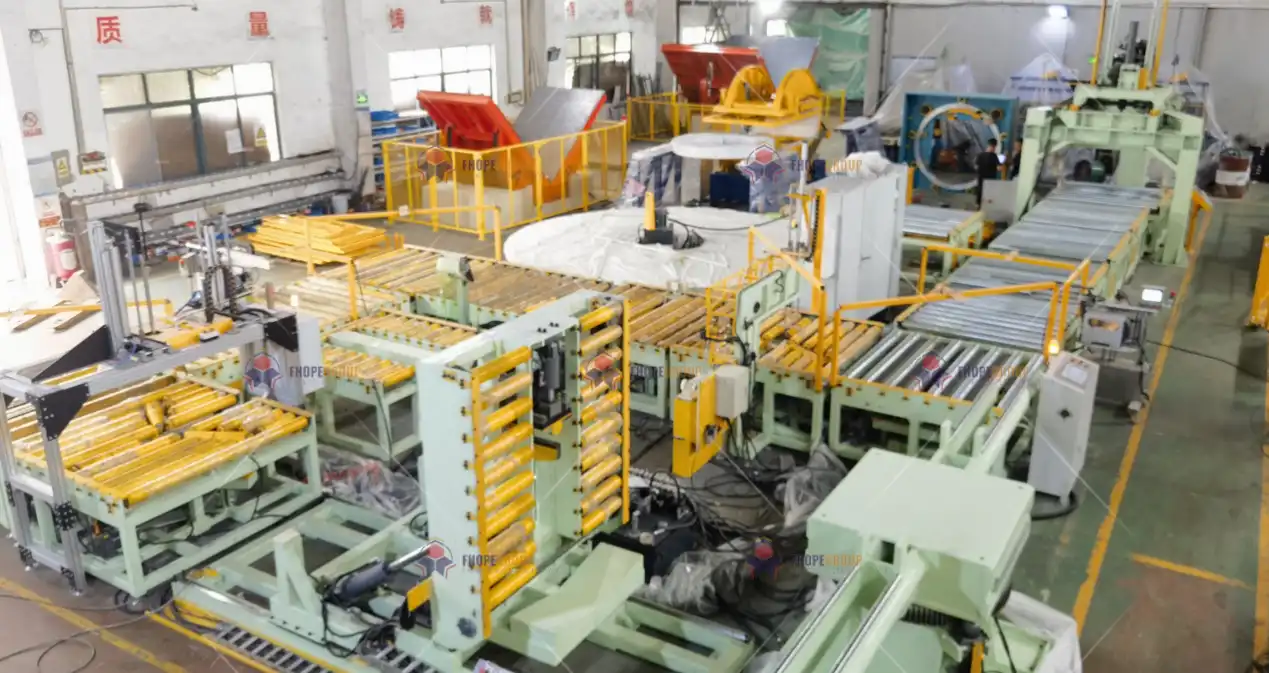

You might be thinking that a strapping head is just a small part of a large packing line. And you're right. But it's the part that does the most critical job: securing your product. Upgrading this single component can have a ripple effect across your entire operation, boosting not just quality but also efficiency and data visibility. Let’s dive deeper into how these advanced heads work and the specific benefits they can bring to a modern steel mill, especially in a dynamic market like Indonesia.
Why is Consistent Strap Tension Crucial for Indonesian Steel Coil Integrity?
Have you ever visited a customer's site and seen one of your steel coils that looks like a collapsed telescope? The inner wraps have slid out, making the coil unstable and often impossible for your customer to process. This "telescoping" is a direct result of improper strap tension. Too loose, and the coil shifts during handling. Too tight, and you risk damaging the edges of the steel, especially with softer materials. This isn't just a minor quality issue; it’s a failure that can lead to rejected shipments and force you to issue credit notes. The source of this inconsistency is very often an outdated strapping head that simply cannot apply the same force, coil after coil.
Consistent strap tension is crucial for Indonesian steel coil integrity because it is the primary force preventing coil telescoping during handling and transport. Correct and uniform tension secures the coil's structure as a single, solid unit. It holds the wraps tightly together without applying excessive force that could crimp or damage the valuable coil edges. This ensures the coil arrives at the customer in perfect, ready-to-use condition, which protects the steel mill's reputation for high quality.

The Mechanics of Precision Tensioning
The secret to consistent tension lies in the technology driving the strapping head. Older systems often relied on pneumatic or hydraulic cylinders, which are prone to fluctuations. Air pressure can drop, and hydraulic fluid temperature can change, altering the force applied. Modern strapping heads have moved beyond this. They use electric servo motors. A servo motor is incredibly precise. It can be programmed to turn a specific number of rotations, which translates to a very exact amount of strap tension. This process is controlled by a feedback loop. A sensor, often a load cell, measures the real-time tension on the strap. This information is sent back to the controller, which instantly adjusts the servo motor to hit the exact target tension, down to the Newton. This means that whether it's the first coil of the day or the last, the tension applied is identical.
The Real Cost of Inconsistent Tensioning
When I work with plant owners, I always encourage them to look at the numbers. The initial investment in an advanced strapping head can seem high, but it pales in comparison to the long-term costs of poor quality. I once worked with a client in Jakarta whose team spent hours each week documenting and processing claims for telescoped coils. The financial loss was significant, but the damage to their relationship with a key automotive customer was even more worrying. We analyzed their packing line and found their old strapping heads had a tension variance of over 25%. After we installed new heads with servo-controlled tensioning, their damage claims dropped to nearly zero within three months. The ROI was clear and fast.
Let's look at a simple comparison:
| Metric | Old Pneumatic Strapping Head | Advanced Servo-Driven Head |
|---|---|---|
| Tension Control | Variable, affected by air pressure | Precise, feedback loop control |
| Coil Damage Rate | 2-5% (telescoping, edge damage) | <0.5% |
| Rework/Re-strapping | Frequent, requires manual labor | Rare, automated consistency |
| Customer Claims | A consistent operational cost | Drastically reduced or eliminated |
| Business Impact | Lost revenue, damaged reputation | Improved profitability, stronger partnerships |
For a steel mill owner, managing costs and ensuring quality are top priorities. Investing in technology that guarantees consistent strap tension is a direct investment in both of these goals. It’s a foundational step to producing a package you can be proud of.
How Does Advanced Sealing Technology Reduce Operational Costs and Waste?
Think about the strap around a heavy steel coil. Its strength is not just in the strap itself, but in the joint that holds it together. If that seal fails, the entire strap is useless, and your coil is no longer secure. Many older packing lines use methods that are either wasteful or unreliable. They might use separate metal clips, which are an ongoing consumable cost and can scratch the coil. Or they use simple heat-sealing methods that consume a lot of energy and often create a weak, inconsistent joint. These small, hidden costs add up quickly. Each failed seal means wasted strap material, wasted energy, and the lost time of an operator who has to re-strap the coil. It's a quiet drain on your profit margin.
Advanced sealing technology, such as friction-weld sealing, reduces operational costs by creating a very strong and reliable joint without requiring expensive metal seals. This modern method consumes significantly less energy than older heat-seal systems because it generates heat through friction only where it's needed. By creating a more consistent and stronger seal, it also minimizes strap waste from failed joints, directly lowering both material and utility expenses on your Indonesian steel coil packing line.

Friction-Weld Sealing Explained
Friction-weld technology has become the standard in high-quality strapping heads for a reason. The process is simple but very effective. After the strap is tensioned around the coil, the two ends of the PET or PP strap are overlapped inside the strapping head. A small vibrating plate, or sonotrode, then presses the straps together and vibrates at a high frequency. This intense friction melts the surfaces of the plastic. The vibration stops, the plastic cools almost instantly, and the two ends are fused into a single, solid piece. This creates a seal that typically retains 85-90% of the original strap's breaking strength, which is far superior to many other methods. Because the heat is localized and generated by friction, the energy required is minimal compared to a heating element that must stay hot all day.
Quantifying the Savings
As an engineer who built a business, I always focus on the return on investment. The move to friction-weld sealing is not just a quality improvement; it's a smart financial decision. It addresses key challenges like fluctuating energy costs and the constant pressure to reduce operational overhead. Let's break down the comparison between different sealing methods you might find on a packing line.
| Feature | Friction-Weld Sealing | Metal Clip Sealing | Traditional Heat Sealing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consumable Cost | None (strap only) | High (constant purchase of clips) | None (strap only) |
| Energy Consumption | Low (only during the sealing cycle) | None | High (heating element is always on) |
| Seal Strength | Very High (85-90% of strap strength) | Medium (depends on clip quality) | Variable (affected by heat/dwell) |
| Risk of Damage | Low (smooth joint) | High (metal clip can scratch coil) | Low |
| Waste | Minimal (very few failed seals) | Low (if sealer is maintained) | High (inconsistent seals lead to re-strapping) |
| Overall Cost | Lowest | Highest | Medium |
For a large steel mill producing thousands of coils, eliminating the cost of metal seals alone can save tens of thousands of dollars per year. When you add the energy savings and the reduction in wasted strap material, the financial argument becomes very powerful. This is the kind of practical innovation that turns a cost center like packaging into a source of efficiency and savings.
What Role Does Data and Automation in Strapping Heads Play in Digital Transformation?
In many older steel mills I've visited, the packing line machinery operates in a black box. The machines do their job, but they don't communicate. You don't know how many cycles a strapping head has performed, if its performance is degrading, or if it's about to fail. This lack of information makes it impossible to move from a reactive maintenance model to a predictive one. For a CEO or plant manager trying to hit an ambitious goal like 95% equipment uptime, this "blind spot" is a major obstacle. Unexpected downtime on a critical line like coil packing can create a bottleneck that disrupts the entire production schedule and delays shipments.
Data and automation in modern strapping heads play a central role in a mill's digital transformation. They act as intelligent data points on the factory floor. These smart heads are equipped with sensors that track key performance indicators like cycle counts, applied tension, and fault histories in real time. This data can be fed directly into a Manufacturing Execution System (MES) or an IoT platform. This enables predictive maintenance scheduling, provides a clear, visual overview of the entire production process, and helps managers make data-driven decisions to boost efficiency and achieve uptime goals.
Moving from Reactive to Predictive Maintenance
The most immediate benefit of a "smart" strapping head is the shift in maintenance strategy. Instead of waiting for a part to break, you can predict when it will need service. It’s the difference between an emergency stop and a planned, scheduled activity. A smart head tracks its own health. For example, it counts every single strapping cycle. You can set a maintenance alert after, say, 250,000 cycles for a specific wear part. The system will notify your maintenance team well in advance. Sensors can also monitor the motor's current draw. A rising trend could indicate that a bearing is beginning to fail. This allows you to order the part and schedule the replacement during a planned shutdown, completely avoiding unexpected downtime. This is exactly what managers need to increase the effective running time of their equipment.
Seamless Integration with Plant-Wide Systems
Digital transformation is about connecting islands of automation into a single, cohesive system. A modern strapping head is designed to do just this. It speaks the language of the modern factory, using communication protocols like Profinet, EtherNet/IP, or OPC-UA. This allows for two-way communication. The plant's MES can send a "recipe" to the strapping head. For example, when the system identifies a specific coil type, it tells the strapping machine: "This is a 1.2-meter wide, high-strength steel coil for an automotive customer. Apply 4 radial straps with 2500 Newtons of tension." The strapping head executes the command and then sends data back, confirming: "4 straps applied successfully, average tension 2505 Newtons, cycle time 15 seconds." This data provides total visibility and traceability for every coil you produce.
Let’s see how this data supports key business goals:
| Data Point from Strapping Head | How It's Used | Business Goal Supported |
|---|---|---|
| Cycle Count | Schedule proactive parts replacement. | Increase Uptime, Predictive Maintenance |
| Real-Time Tension Data | Verify that every strap meets quality specs. | Enhance Quality, Reduce Claims |
| Fault/Error Codes | Diagnose problems quickly without guesswork. | Reduce Downtime, Improve Efficiency |
| Recipe Confirmation | Create a digital record for each coil. | Digital Transformation, Traceability |
| Motor Current/Temperature | Monitor component health and predict failures. | Lower Maintenance Costs, Uptime |
For a forward-thinking leader, this technology is not just about strapping coils. It’s about gathering the intelligence needed to run a smarter, more efficient, and more profitable factory. It turns a simple machine into a valuable asset in your digital strategy.
How Can Modern Strapping Heads Adapt to Diverse Coil Specifications in Indonesia's Market?
The steel market in Indonesia, like many others, is driven by the shifting demands of downstream industries like construction and automotive. One week, your order book might be full of wide, heavy-gauge coils. The next, you might need to produce small, narrow coils for a specialized manufacturer. In a facility with older equipment, each of these changeovers is a major event. It means stopping the line while operators manually adjust mechanical guides, change settings, and run test cycles. This downtime is a direct hit to your productivity and makes it difficult to respond quickly to new market opportunities. It becomes a bottleneck that limits your plant's agility and overall capacity.
Modern strapping heads are engineered specifically for this kind of flexibility. They adapt to diverse coil specifications through automation and programmable "recipes." An operator can select the next product type on a simple HMI screen, and the machine automatically adjusts the strap positions, tension levels, and the number of straps applied per coil. This technology allows Indonesian steel mills to switch between different production runs in minutes, not hours, minimizing downtime and maximizing the plant's ability to serve a fluctuating market.

The Power of Programmable Strapping Recipes
The core of this adaptability is the concept of a "recipe." For every type of coil you produce, you can create and save a specific strapping program. This recipe contains all the necessary parameters: the coil's diameter and width, the number of radial straps required (e.g., 3, 4, or 6), the precise tension for each strap, and the exact positions where the straps should be applied. When a new coil type arrives at the strapping station, a sensor can read a barcode, or an operator can simply select the corresponding recipe from a touchscreen menu. The machine then takes over. The strapping head and the lance that feeds the strap around the coil automatically reposition themselves for the new coil dimensions. The entire changeover can happen in under a minute, with no manual tools required.
Physical Design for Maximum Flexibility
This automation is supported by smart physical design. Many advanced strapping heads are mounted on a "floating" or movable carriage. This allows the head to move vertically and horizontally to find the ideal strapping position, even if the coil isn't perfectly centered on the conveyor. This is a huge advantage over older, fixed-head systems that would often fail a strapping cycle if the coil was slightly misaligned. This ability to accommodate small variations in coil placement reduces errors, minimizes rework, and keeps the line moving. It builds a higher tolerance for real-world conditions into your process.
Let's compare the changeover process directly:
| Changeover Task | Old, Manual Machine | Modern, Automated Machine |
|---|---|---|
| Adjusting for Coil Width | Stop line, use wrenches to move guides. (30+ min) | Automatic adjustment via recipe selection. (<1 min) |
| Changing Strap Pattern | Mechanical adjustment of strap positions. (15+ min) | Select new recipe on HMI. (Instant) |
| Setting Strap Tension | Manual adjustment, trial and error. | Tension value is part of the digital recipe. |
| Operator Skill Required | High, requires experienced mechanic. | Low, simple menu selection. |
| Total Downtime | 45-60 minutes per changeover | < 2 minutes per changeover |
In my experience, this level of automation is a game-changer for mills that need to be agile. It directly supports the goal of increasing capacity utilization by converting downtime into productive uptime. It gives a business the power to say "yes" to more customers and more diverse orders, knowing their packing line can handle the variation without missing a beat.
Conclusion
Ultimately, advanced strapping heads are not just equipment. They are a strategic investment in quality, efficiency, and future-proofing your Indonesian steel packing line for higher profitability.





